What Is The Science Behind BFR?
B3 Bands Are Backed by Extensive Science and Research
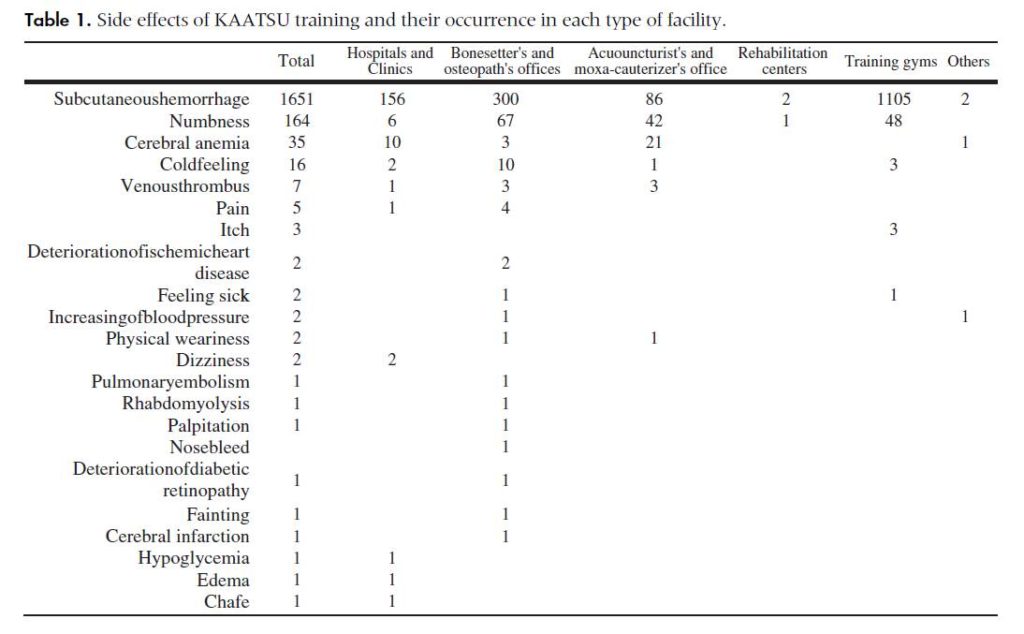
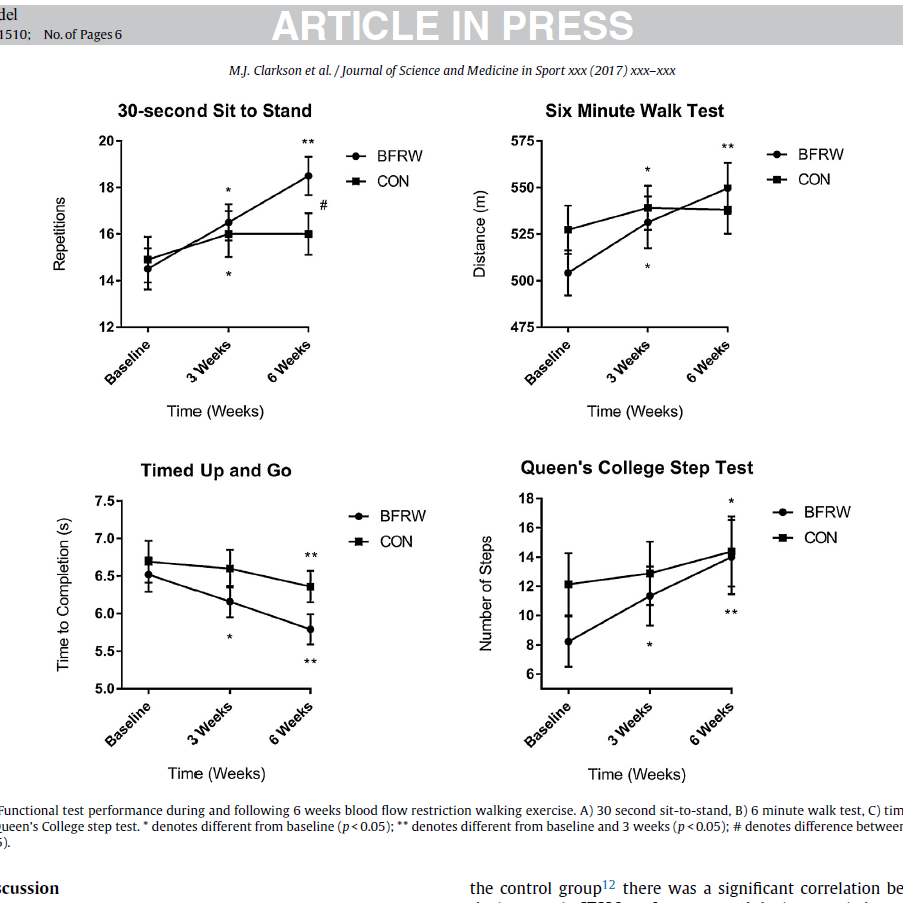
BFR training is supported by extensive research and scientific evidence demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing muscle strength, hypertrophy, and endurance with significantly lower training intensities compared to traditional methods.
The science behind BFR training highlights its potential for improving athletic performance, aiding in rehabilitation, and providing a safer, more accessible option for individuals across various age groups and fitness levels.
B3 Bands Multi-Air Chamber Design

Innovative Multi-Air Chamber Design
B3 offers one of the only Multi-Air Chamber Bands on the market, a patented technology that sets us apart in the field of BFR. This advanced design ensures that our B3 Bands do not create a tourniquet effect, which is a common concern with traditional BFR bands. Our unique chambers distribute pressure evenly, making the bands safe and effective.
Safety and Comfort
One of the primary benefits of our Multi-Air Chamber design is that it does not require a Doppler to measure blood flow. This feature simplifies the use of B3 Bands, making them accessible to everyone from beginners to seasoned athletes. Safety is our top priority, and our bands are as safe as normal exercise for individuals ranging from 9 to 90 years old.
In addition to safety, our bands are recognized as #1 for comfort, allowing users to focus on their workout without the discomfort often associated with other BFR bands.
Videos
Watch Video from Dr. Jim Stray-Gundersen demonstrating how B3 Bands do not cut off blood flow
Watch Video of Dr. Mike DeBord comparing B3 Bands to the other bands on the market
B3 Bands Are Trusted and Effective

Endorsement by Elite Athletes
The effectiveness of B3 Bands is further highlighted by their preference among USA Olympic teams and other professional athletes. These elite athletes trust B3 Bands to enhance their performance, indicating the superior quality and benefits of our product.
The Most Effective BFR Bands
When you combine ease of use, safety, comfort, and extensive research the result is the most effective BFR Bands for exercise, rehabilitation, and athletic performance. B3 Bands provide a comprehensive solution that meets the needs of a diverse range of users, from young athletes to older adults seeking safe and effective ways to maintain fitness and mobility.
Is BFR Safe?
Yes, Blood Flow Restriction (BFR) training is considered safe when used correctly. Research has shown that BFR training, particularly with high-quality bands like B3 Bands, does not create a tourniquet effect and ensures an even distribution of pressure. This design minimizes risks and makes BFR as safe as normal vigorous exercise. BFR training is suitable for a wide range of individuals, from young athletes to older adults, and has been endorsed by professionals and elite athletes for its safety and effectiveness.
Always consult with your doctor before beginning any exercise or rehab program.
Check out the articles below for a sampling of BFR research.